Shineyrock
blog
- dislike -1
Dynamic Page Templates in WordPress, Part 3
In the first two parts of this tutorial series, we covered what dynamic page templates were and why they were needed. We also looked at the code required to implement them.
In this third and final tutorial in the series, I'll be creating two examples of fully working dynamic page templates you can use in your own projects. These were specifically chosen to be easily extendable to suit your own needs, and are intended as inspiration for any other type of dynamic page templates you can think of.
The two dynamic page templates we'll be taking a look at shortly are:
- Simple Contact Form
- Blog Post Archive
As well as implementing our page templates, I'll also show you how to add extra polish, via custom CSS and JavaScript, to make interaction much more intuitive to end users.
Plus, we'll take a look at how you can use page templates for any post type. Since WordPress 4.7, you can specify the post type a page template is associated with. We'll see how you can modify an existing dynamic page template to take advantage of this new feature so it works with any post type.
We've a lot to cover in this tutorial, so let's get started!
Theme Setup
We'll be using a WordPress Twenty Seventeen child theme again, just as we did in part 2 of this tutorial series, to add our dynamic page template code. Let's begin with a blank child theme.
Create a child theme folder called
twentyseventeen-childand add the following files:- functions.php
- style.css
Inside
style.css, add:/* Theme Name: Twenty Seventeen Child Description: Twenty Seventeen Child Theme Author: David Gwyer Template: twentyseventeen Version: 0.1 License: GNU General Public License v2 or later License URI: http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-2.0.html Text Domain: twenty-seventeen-child */
And inside
functions.php, add:<?php /** * Twenty Seventeen child theme class. * * DPT = D[ynamic] P[age] T[emplates]. */ class DPT_Twenty_Seventeen_Child { /** * Register hooks. */ public function init() { add_action( 'wp_enqueue_scripts', array( $this, 'enqueue_parent_theme_styles' ) ); } /* Enqueue parent theme styles. */ public function enqueue_parent_theme_styles() { wp_enqueue_style( 'twenty-seventeen-css', get_template_directory_uri() . '/style.css' ); } } $ts_child_theme = new DPT_Twenty_Seventeen_Child(); $ts_child_theme->init();Add the child theme to your WordPress theme directory as we did before. If you're not sure about how to do this, please refer back to part 2 in this tutorial series.
We now have a working (blank) child theme ready for us to add our dynamic page template code to.
Dynamic Form Page Template
Our first real implementation of a dynamic page template is a simple contact form. We'll be adding the following fields:
- Heading
- Name
- Subject
- Phone number
These are text input fields, apart from the heading, which is a standard HTML heading tag.
Before we implement the actual page template, though, we need to add custom controls to the page editor that will allow us to modify page template output. Then, when we create the page template, it will be rendered according to the page editor control settings.
In part 2 of this tutorial series, I mentioned that there's no easy way to add custom controls directly to the 'Page Attributes' meta box, where the page template drop-down is located.

This means that we have to add our dynamic page template controls elsewhere for now. I'll show you how to get around this limitation a little later on, with a little CSS and JavaScript magic. But for now, we'll have to make do with adding our custom controls to a separate meta box.
In the
DPT_Twenty_Seventeen_Childclass, register two new action hooks in theinitmethod, and a new method calledpage_template_meta_boxes.<?php /** * Register hooks. */ public function init() { add_action( 'wp_enqueue_scripts', array( $this, 'enqueue_parent_theme_styles' ) ); add_action( 'load-post.php', array( $this, 'page_template_meta_boxes' ) ); add_action( 'load-post-new.php', array( $this, 'page_template_meta_boxes' ) ); } /* Add meta box hook. */ public function page_template_meta_boxes() { add_action( 'add_meta_boxes', array( $this, 'add_page_template_meta_boxes' ) ); }The
load-post.phpandload-post-new.phpaction hooks run whenever a post (of any type) is edited or created. When this happens, we register another action hookadd_meta_boxesthat will trigger the creation of our custom meta box, which is done via theadd_page_template_meta_boxescallback function. Let's implement that function now.<?php /* Register meta box. */ public function add_page_template_meta_boxes() { // Create meta box for our form dynamic page template add_meta_box( 'form-page-template-meta-box', esc_html__( 'Form Page Template Meta Box', 'twenty-seventeen-child' ), array( $this, 'display_form_page_template_meta_box' ), 'page', 'side', 'default' ); }The actual rendering of the meta box controls will be handled via the
display_form_page_template_meta_boxcallback function, which was specified above as one of the arguments toadd_meta_box().<?php /* Render form meta box on the page editor. */ public function display_form_page_template_meta_box( $object ) { ?><p>Add controls here...</p><?php }For now, I've added some placeholder text so we can see our new meta box on the page editor.

Remember from earlier that our form page template will have a heading and four text fields. There are many ways we could choose to customize the form output, but in our case let's add check boxes for each field that will allow us to toggle their visibility. Update
display_form_page_template_meta_box()to include the following code.<?php public function display_form_page_template_meta_box( $object ) { wp_nonce_field( basename( __FILE__ ), 'page_template_meta_box_nonce' ); $heading = get_post_meta( $object->ID, 'pt_chk_form_heading', true ); $name = get_post_meta( $object->ID, 'pt_chk_form_name', true ); $subject = get_post_meta( $object->ID, 'pt_chk_form_subject', true ); $email = get_post_meta( $object->ID, 'pt_chk_form_email', true ); $phone = get_post_meta( $object->ID, 'pt_chk_form_phone', true ); ?> <div id="form_pt_wrapper"> <p> <input type="checkbox" name="pt_chk_form_heading" id="pt_chk_form_heading" value="1" <?php checked( $heading, true ); ?> /> <label for="pt_chk_form_heading"><?php _e( "Display Heading", 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?></label><br> </p> <p> <input type="checkbox" name="pt_chk_form_name" id="pt_chk_form_name" value="1" <?php checked( $name, true ); ?> /> <label for="pt_chk_form_name"><?php _e( "Display Name", 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?></label><br> </p> <p> <input type="checkbox" name="pt_chk_form_subject" id="pt_chk_form_subject" value="1" <?php checked( $subject, true ); ?> /> <label for="pt_chk_form_subject"><?php _e( "Display Subject", 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?></label><br> </p> <p> <input type="checkbox" name="pt_chk_form_email" id="pt_chk_form_email" value="1" <?php checked( $email, true ); ?> /> <label for="pt_chk_form_email"><?php _e( "Display Email", 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?></label><br> </p> <p> <input type="checkbox" name="pt_chk_form_phone" id="pt_chk_form_phone" value="1" <?php checked( $phone, true ); ?> /> <label for="pt_chk_form_phone"><?php _e( "Display Phone Number", 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?></label><br> </p> </div> <?php }We include a nonce field for security which will be verified later on, just before we save the form values into the database.
Note: If for any reason the nonce value cannot be verified then the settings won't be saved.
Then, current form values are retrieved from the database before the custom form fields are outputted inside the meta box.

Currently, our check boxes won't be saved when the post is updated. To make the form settings persist, we need to register a new hook in the
init()method that triggers during asave_postaction, and then implement the callback to manually update post meta settings.<php /** * Register hooks. */ public function init() { add_action( 'wp_enqueue_scripts', array( $this, 'enqueue_parent_theme_styles' ) ); add_action( 'load-post.php', array( $this, 'page_template_meta_boxes' ) ); add_action( 'load-post-new.php', array( $this, 'page_template_meta_boxes' ) ); add_action( 'save_post', array( $this, 'save_page_template_meta' ), 10, 2 ); }<?php /* Save meta box data. */ public function save_page_template_meta( $post_id, $post ) { if ( ! ( isset( $_POST[ 'page_template_meta_box_nonce' ] ) && wp_verify_nonce( $_POST[ 'page_template_meta_box_nonce' ], basename( __FILE__ ) ) ) ) { return $post_id; } if ( ! current_user_can( 'edit_post', $post_id ) ) { return $post_id; } if( 'page' != $post->post_type ) { return $post_id; } $heading = isset( $_POST[ 'pt_chk_form_heading' ] ) ? $_POST[ 'pt_chk_form_heading' ] : ''; update_post_meta( $post_id, 'pt_chk_form_heading', $heading ); $name = isset( $_POST[ 'pt_chk_form_name' ] ) ? $_POST[ 'pt_chk_form_name' ] : ''; update_post_meta( $post_id, 'pt_chk_form_name', $name ); $subject = isset( $_POST[ 'pt_chk_form_subject' ] ) ? $_POST[ 'pt_chk_form_subject' ] : ''; update_post_meta( $post_id, 'pt_chk_form_subject', $subject ); $email = isset( $_POST[ 'pt_chk_form_email' ] ) ? $_POST[ 'pt_chk_form_email' ] : ''; update_post_meta( $post_id, 'pt_chk_form_email', $email ); $phone = isset( $_POST[ 'pt_chk_form_phone' ] ) ? $_POST[ 'pt_chk_form_phone' ] : ''; update_post_meta( $post_id, 'pt_chk_form_phone', $phone ); }Once the form nonce value and user permissions have been verified, along with a check to make sure we are on the correct post type, we can test for the posted form values and safely save the values to the database.
Our check boxes are now fully functional, so we can go ahead and implement the actual page template! Inside the root child theme folder, add a new folder called
page-templates, and add to it a new file calledform-page-template.php.Add the following code to the new file to create a blank page template.
<?php /** * Template Name: Form Page Template * * @package WordPress * @subpackage Twenty_Seventeen * @since 1.0 */ get_header(); ?> <div class="wrap"> <div id="primary" class="content-area"> <main id="main" class="site-main" role="main"> <!-- Add page template code here. --> </main><!-- #main --> </div><!-- #primary --> </div><!-- .wrap --> <?php get_footer();To reduce code complexity, our contact form doesn't validate user input, and we've committed the usual form checks and validation, as we want to focus purely on making the form output dynamic without extraneous code.
First, we need to retrieve the dynamic contact form check box values.
<?php $heading = get_post_meta( get_the_ID(), 'pt_chk_form_heading', true ); $name = get_post_meta( get_the_ID(), 'pt_chk_form_name', true ); $subject = get_post_meta( get_the_ID(), 'pt_chk_form_subject', true ); $email = get_post_meta( get_the_ID(), 'pt_chk_form_email', true ); $phone = get_post_meta( get_the_ID(), 'pt_chk_form_phone', true );
Then we can add in the form code. This is very similar for each form field. Let's take a look at the
namefield code.<?php if ( ! empty ( $name ) ) : ?> <label for="cf_name"><?php _e( 'Name', 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?></label> <input type="text" name="cf_name" id="cf_name"><br> <?php endif; ?>We test the value of the check box from the page template settings and only output the form field if it's checked. Otherwise, nothing gets outputted. This is repeated for each form field.
Once the form is submitted, we send an email to the site admin and display a message on screen. Putting this all together, we have our final page template code.
<?php /** * Template Name: Form Page Template * * @package WordPress * @subpackage Twenty_Seventeen * @since 1.0 */ get_header(); ?> <div class="wrap"> <div id="primary" class="content-area"> <main id="main" class="site-main" role="main"> <?php while ( have_posts() ) : the_post(); $heading = get_post_meta( get_the_ID(), 'pt_chk_form_heading', true ); $name = get_post_meta( get_the_ID(), 'pt_chk_form_name', true ); $subject = get_post_meta( get_the_ID(), 'pt_chk_form_subject', true ); $email = get_post_meta( get_the_ID(), 'pt_chk_form_email', true ); $phone = get_post_meta( get_the_ID(), 'pt_chk_form_phone', true ); // Form submission handler if ( isset( $_POST['cf_submitted'] ) ) { $admin_email = get_bloginfo( 'admin_email' ); $cf_subject = trim( $_POST['cf_subject'] ); $headers = "From: me@mysite.com\r\n"; mail( $admin_email, $subject, 'Dynamic contact form submitted!', $headers ); echo "<p>Mail sent successfully!</p>"; } ?> <form action="<?php the_permalink(); ?>" method="post"> <?php if ( ! empty( $heading ) ) : ?> <h2>Dynamic Form Page Template!</h2> <?php endif; ?> <?php if ( ! empty( $name ) ) : ?> <label for="cf_name"><?php _e( 'Name', 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?></label> <input type="text" name="cf_name" id="cf_name"><br> <?php endif; ?> <?php if ( ! empty( $subject ) ) : ?> <label for="cf_subject"><?php _e( 'Subject', 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?></label> <input type="text" name="cf_subject" id="cf_subject"><br> <?php endif; ?> <?php if ( ! empty( $email ) ) : ?> <label for="cf_email"><?php _e( 'Email', 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?></label> <input type="email" name="cf_email" id="cf_email"><br> <?php endif; ?> <?php if ( ! empty( $phone ) ) : ?> <label for="cf_phone"><?php _e( 'Phone Number', 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?></label> <input type="tel" name="cf_phone" id="cf_phone"><br> <?php endif; ?> <p><input type="hidden" name="cf_submitted" id="cf_submitted" value="true"><input class="submit button" type="submit" value="<?php _e( 'Submit Form', 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?>"></p> </form> <?php endwhile; // End of the loop. ?> </main><!-- #main --> </div><!-- #primary --> </div><!-- .wrap --> <?php get_footer();To test everything's working correctly, make sure all the form page template check boxes are checked and update the post. Then take a look at the page template on the front end.
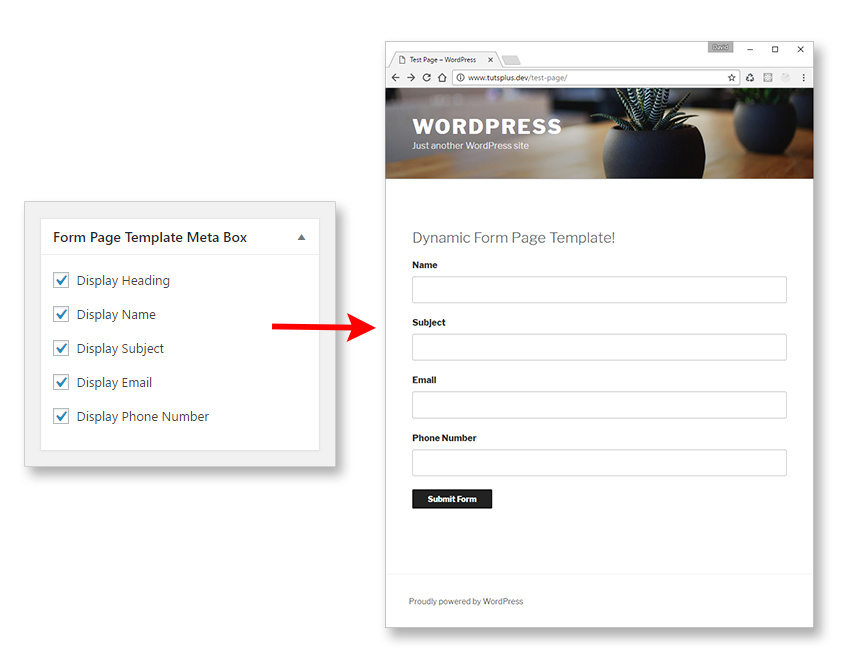
Now try unchecking some of the form page template check boxes. Only the fields specified are outputted. You have total control over how the form is displayed! In the screen shot below, I unchecked just the email and phone check boxes.

Note: If you're working on a local WordPress environment then the
mailfunction may not actually send the email. It will only work if you have a mail server set up and running.The form could easily be extended to add any number of controls of any type. For example, you could add an optional CAPTCHA field to your form, or be able to specify the order of fields outputted, or even the text for the form heading/labels. The point here is that you can use dynamic page templates to customize your form however you want. The possibilities are literally endless!
Organizing Our Page Template Controls
You might have noticed that there are a couple of usability issues with the admin controls for our dynamic page template. Functionally it's fine, but ideally the dynamic page template controls should be in the same meta box as the page template drop-down.

Remember that the reason we had to add our page template controls to a separate meta box in the first place was because there's currently no WordPress hook available to add custom controls directly to the page template meta box.
Also, when a dynamic page template is selected, we only want the controls associated with that template to be visible. We can complete both requirements by adding some custom CSS and JavaScript to the page editor.
Specifically, we need to:
- Hide the form meta box.
- Wait for the admin editor page to fully load.
- Move the form controls to the 'Page Attributes' meta box.
- Only display the admin form controls if the associated page template is selected.
Start by adding
cssandjsfolders to your child theme root folder. Inside thecssfolder create astyle.cssfile, and in thejsfolder create ascript.jsfile. You can call these anything you want, though. Just remember to make a note of the filenames if so, and replace them in the enqueue scripts code.Then, we need to enqueue both files only on the page editor screen. We don't want them added to all admin pages. Register a new action hook in the
init()method to load scripts on admin pages, and add the callback function to enqueue the script files.<?php /** * Register hooks. */ public function init() { add_action( 'wp_enqueue_scripts', array( $this, 'enqueue_parent_theme_styles' ) ); add_action( 'load-post.php', array( $this, 'page_template_meta_boxes' ) ); add_action( 'load-post-new.php', array( $this, 'page_template_meta_boxes' ) ); add_action( 'save_post', array( $this, 'save_page_template_meta' ), 10, 2 ); add_action( 'admin_enqueue_scripts', array( $this, 'enqueue_editor_scripts' ) ); } public function enqueue_editor_scripts($hook) { global $post_type; if ( 'page' != $post_type ) { return; } if ( 'post-new.php' != $hook && 'post.php' != $hook) { return; } wp_enqueue_script( 'dpt_script', get_stylesheet_directory_uri() . '/js/script.js', array( 'jquery' ) ); wp_enqueue_style( 'dpt_styles', get_stylesheet_directory_uri() . '/css/style.css' ); }Notice how we're targeting the
pagepost type and then either thepost-new.phporpost.phpadmin pages. So, basically, unless we're on the page editor, our scripts will not get loaded, which is what we want.Let's go ahead now and start adding CSS and JavaScript to customize the form page template controls. Firstly, hide the whole form meta box with CSS by adding this to
style.css:#form-page-template-meta-box { display: none; }We could have done this with JavaScript, but we want the form meta box to be hidden immediately. If we did it via JavaScript, we'd have to wait until the page loaded, and you'd see a small flash as the meta box rendered on screen and then was hidden with JavaScript. So using CSS in this case is better.
Now for the JavaScript. Add this to
script.js.jQuery(document).ready(function ($) { var pt = $( "#page_template" ); var form_controls = $( "#form_pt_wrapper" ); // Move form controls to 'Page Attributes' meta box and hide them by default form_controls.insertAfter( '#page_template' ).hide(); function displayControls( ptStr, sel ) { if ( ptStr !== pt.val() ) { sel.hide(); } else { sel.toggle(); } } // Call on page load displayControls( 'page-templates/form-page-template.php', form_controls ); // Call every time drop down changes pt.on( 'change', function () { displayControls( this.value, form_controls ); }); });I'm not going to go into a huge amount of detail regarding the JavaScript, but here's the overview.
We first cache a couple of CSS selectors and move the admin form controls to the
Page Attributesmeta box. Then, we have adisplayControls()function that either hides or displays the form controls depending on the current value of the page template drop-down. We calldisplayControls()on page load, and then every time the drop-down is changed, to make sure we're always in sync.With the CSS and JavaScript added, the form page template controls are now displayed in the correct meta box, and only show if the associated page template is selected.

This looks much better and is way more intuitive to the user. Because meta boxes can be moved around WordPress admin screens, our dynamic page template controls would not necessarily have been anywhere near the page template drop-down! We've solved this problem in an elegant way to ensure our controls always appear directly underneath the page template drop-down!
Blog Posts Dynamic Page Template
Our next dynamic page template displays a list of your latest blog posts. But rather than just list all posts, we'll implement a list box (similar to a drop-down) to allow you to choose the post category. Not only that, you'll also be able to select multiple post categories.
Start by adding a new meta box in
add_page_template_meta_boxes().<?php // Create meta box for our blog posts dynamic page template add_meta_box( 'blog-page-template-meta-box', esc_html__( 'Blog Page Template Meta Box', 'twenty-seventeen-child' ), array( $this, 'display_blog_page_template_meta_box' ), 'page', 'side', 'default' );And now we need to implement the callback function to render our meta box.
<?php /* Render form meta box on the page editor. */ public function display_blog_page_template_meta_box( $object ) { $blog_category = get_post_meta( $object->ID, 'blog_category', true ); $categories = get_categories(); ?> <div id="blog_pt_wrapper"> <label for="blog_category[]"><?php _e( 'Choose categories', 'twenty-seventeen-child' ); ?>:</label> <select style="height:inherit;" name="blog_category[]" multiple="multiple" size="10"> <?php foreach ( $categories as $category ) { printf( '<option value="%1$s" %2$s>%3$s (%4$s)</option>', esc_attr( $category->cat_ID ), esc_attr( selected( $category->cat_ID, $this->q($category->cat_ID, $blog_category) ) ), esc_html( $category->cat_name ), esc_html( $category->category_count ) ); } ?> </select> </div> <?php }Let's break this down. We first define a variable to hold the list of post categories selected (if any) from the last time the post was updated. Another variable stores an array of all existing categories.
Note: We already have a nonce field from our previous form page template, so we don't need to use another one here, as we are on the same admin page.
We then loop over the list of the site categories, populating a drop-down control as we go. Any category that was previously selected is selected again to keep everything in sync.
You might have noticed, though, that one of the arguments to
selected()is a function call. Normally we just useselected()to compare two values to determine whether to mark the current item as selected. However, because we can select more than one category, our database setting is always an array of values (even if we actually only select one category).The function
q()is a helper function which allows us to check the current list item against the array of saved categories.<?php public function q($sel, $opt) { if( is_array($opt) && in_array($sel, $opt) ) { return $sel; } }For each category, the category ID is passed into
q()along with the saved category array. If the current category is in the list of saved categories then the current category is returned toselected()and will match the first argument. This will causeselected()to mark the current category as selected. This is an elegant way of handling multiple options for a single control.All we need to do now is update
save_page_template_meta()to handle saving blog post categories. Add this code to do just that.<?php // Save blog page template controls $category = isset( $_POST[ 'blog_category' ] ) ? $_POST[ 'blog_category' ] : ''; update_post_meta( $post_id, 'blog_category', $category );
Now, we need to create the blog posts page template. Inside your child themes
page-templatesfolder, create a new file calledblog-page-template.php, and add the following code.<?php /** * Template Name: Blog Page Template * * @package WordPress * @subpackage Twenty_Seventeen * @since 1.0 */ get_header(); ?> <div class="wrap"> <div id="primary" class="content-area"> <main id="main" class="site-main" role="main"> <?php $paged = ( get_query_var('paged') ) ? get_query_var('paged') : 1; $category = get_post_meta( get_the_id(), 'blog_category', true ); if( is_array($category) ) { $category = implode(",", $category); } if( !empty($category) ) { $cat = $category; } else { $cat = 0; } $query_args = array( 'paged' => $paged, 'cat' => $cat, 'orderby' => 'date', 'order' => 'DESC', 'post_type' => 'post' ); $blog_posts = new WP_Query($query_args); ?> <?php if ( $blog_posts->have_posts() ) : ?> <?php while ( $blog_posts->have_posts() ) : $blog_posts->the_post(); ?> <?php get_template_part( 'template-parts/post/content', get_post_format() ); ?> <?php endwhile; // end of the loop. ?> <?php endif; ?> </main><!-- #main --> </div><!-- #primary --> </div><!-- .wrap --> <?php get_footer();The only real difference from our previous dynamic page template is the code inside the
<main>HTML tag, so let's take a closer look at that now.We first set the value of the
pagedquery variable, which is used to display posts over multiple pages, depending on the number of pages returned from our WordPress query. Then, we get the all the categories selected on the page editor meta box. The category array is converted to a string and given a default value if empty. A new WordPress query is then created and the results outputted in a standard loop.The key thing here is that we're able to control exactly which categories are passed to the query object, via the selections made on the page editor meta box.
All we have to do now is hide the blog categories meta box and move the list control to the
Page Attributesmeta box. Just like we did before.Inside
style.cssupdate the styles to hide the blog posts meta box:#form-page-template-meta-box, #blog-page-template-meta-box { display: none; }The
script.jsfile needs a little more code to be added. Here is the fully updated file.jQuery(document).ready(function ($) { var pt = $( "#page_template" ); var form_controls = $( "#form_pt_wrapper" ); var blog_post_controls = $( "#blog_pt_wrapper" ); // Move form controls to 'Page Attributes' meta box and hide them by default form_controls.insertAfter( '#page_template' ).hide(); blog_post_controls.insertAfter( '#page_template' ).hide(); function displayControls( ptStr, sel ) { if ( ptStr !== pt.val() ) { sel.hide(); } else { sel.toggle(); } } // Call on page load displayControls( 'page-templates/form-page-template.php', form_controls ); displayControls( 'page-templates/blog-page-template.php', blog_post_controls ); // Call every time drop down changes pt.on( 'change', function () { var controls; if( this.value === 'page-templates/form-page-template.php' ) { controls = form_controls; blog_post_controls.hide(); } else if( this.value === 'page-templates/blog-page-template.php' ) { controls = blog_post_controls; form_controls.hide() } else { // hide all blog_post_controls.hide() form_controls.hide(); } displayControls( this.value, controls ); }); });Most of the changes worth noting are in the
.on('change')function. Because we now have more than one dynamic page template, we have to test to see which one was selected from the drop-down, and then pass this in the corresponding element selector todisplayControls().We also need to hide all other page template controls apart from the one selected. And if the default page template is displayed, we hide all page template controls. The JavaScript code could be optimized further, but as we only have two dynamic page templates active, it does a good enough job for our needs.

With these modifications in place, we now have two functioning dynamic page templates with each of their associated controls displayed directly underneath the page template drop-down.
Page Templates for Everyone
Earlier I alluded to how, in WordPress 4.7+, you can now assign page templates to any post type. Prior to WordPress 4.7, you could only assign them to pages, but not anymore!
All you have to do is add an extra line to the comment block in the page template header, and specify a comma-separated list of post types you want the page template to be available on.
<?php Template Post Type: page, movie, notes
The post type name needs to be the same as the slug entered when the post type was first registered, otherwise it will be ignored.
So, we can display page templates for any post type, but what about dynamic page templates? With just a few modifications, these can be supported too. Let's take a look at what's needed.
Luckily, apart from adding a line of code the top of your page template, all the necessary changes are in one file:
functions.php.Firstly, we need to enqueue the dynamic page template CSS and JavaScript not just on pages but for all post types we want to support dynamic page templates. So, in
enqueue_editor_scripts(), we can do something like this.<?php if ( 'page' != $post_type && 'movie' != $post_type ) { return; }Now, the dynamic page template scripts will be loaded on pages and the movie custom post type.
Next, in
add_page_template_meta_boxes(), update each instance ofadd_meta_box()you want to show on a custom post type. Instead of just specifyingpage, we can pass in an array of required post types.<?php add_meta_box( 'form-page-template-meta-box', esc_html__( 'Form Page Template Meta Box', 'twenty-seventeen-child' ), array( $this, 'display_form_page_template_meta_box' ), Array( 'page', 'movie' ), 'side', 'default' );Finally, update
save_page_template_meta()to support multiple post types just as we did forenqueue_editor_scripts(). And that's it!By just following these few short steps, you can modify your dynamic page templates to work for any post type.
Note: For any WordPress sites running less than version 4.7, the
Template Post Typeheader text will simply be ignored, and all page templates will be displayed for pages by default. If this is not desirable, you can add custom code to make your page templates backwards compatible.<?php function makewp_exclude_page_templates( $post_templates ) { if ( version_compare( $GLOBALS['wp_version'], '4.7', '<' ) ) { unset( $post_templates['templates/my-full-width-post-template.php'] ); } return $post_templates; } add_filter( 'theme_page_templates', 'makewp_exclude_page_templates' );This snippet is taken from the Make WordPress blog, where you can find more information about backwards compatibility and the new page templates feature in more detail.
Conclusion
We've covered quite a bit of ground in the final part of this tutorial series. Specifically, we've implemented two fully working dynamic page templates and used custom CSS and JavaScript to add some polish to the user experience.
Even though the dynamic post types introduced in this tutorial series have been relatively simple, it would be very easy to extend them to create powerful and flexible page templates. There's just so much scope to add some next-level functionality. And, from WordPress 4.7, you're not limited to developing them just for pages either.
If you're looking for other utilities to help you build out your growing set of tools for WordPress or for code to study and become more well-versed in WordPress, don't forget to see what we have available in Envato Market.
Has this tutorial series inspired you to create dynamic page templates? If so, let me know in the comments below. I'd love to hear your ideas and how you might use them in your own projects.

martijn broeders
founder/ strategic creative bij shineyrock web design & consultancy
e-mail: .(JavaScript must be enabled to view this email address)
telefoon: 434 210 0245
Per - categorie
Op - datum
December, 2023
The Best Small Business Web Designs by DesignRush
/ -2
-2October, 2022
Create Modern Vue Apps Using Create-Vue and Vite
/ 5
5September, 2022
Pros and Cons of Using WordPress
/ -3
-3How to Fix the “There Has Been a Critical Error in Your Website” Error in WordPress
/ 1
1How To Fix The “There Has Been A Critical Error in Your Website” Error in WordPress
/ -2
-2August, 2022
How to Create a Privacy Policy Page in WordPress
/ 1
1April, 2022
How Long Does It Take to Learn JavaScript?
/ 1
1January, 2022
The Best Way to Deep Copy an Object in JavaScript
/ -1
-1December, 2021
-
/
 5
5 -
/
 -4
-4 Adding and Removing Elements From Arrays in JavaScript
/ 3
3Create a JavaScript AJAX Post Request: With and Without jQuery
/ 5
5November, 2021
5 Real-Life Uses for the JavaScript reduce() Method
/ -2
-2July, 2021
How to Enable or Disable a Button With JavaScript: jQuery vs. Vanilla
/ 7
7How to Enable or Disable a Button With JavaScript: jQuery vs Vanilla
/ -8
-8Confirm Yes or No With JavaScript
/ -1
-1June, 2021
How to Change the URL in JavaScript: Redirecting
/ -4
-415+ Best WordPress Twitter Widgets
/ -2
-2May, 2021
27 Best Tab and Accordion Widget Plugins for WordPress (Free & Premium)
/ 14
1421 Best Tab and Accordion Widget Plugins for WordPress (Free & Premium)
/ -4
-430 HTML Best Practices for Beginners
/ -5
-531 Best WordPress Calendar Plugins and Widgets (With 5 Free Plugins)
/ -4
-425 Ridiculously Impressive HTML5 Canvas Experiments
/ -3
-3-
/
 4
4 How to Implement Email Verification for New Members
/ 2
2How to Create a Simple Web-Based Chat Application
/ 4
4April, 2021
30 Popular WordPress User Interface Elements
/ -2
-2Top 18 Best Practices for Writing Super Readable Code
/ 5
5Best Affiliate WooCommerce Plugins Compared
/ -4
-4March, 2021
18 Best WordPress Star Rating Plugins
/ 8
810+ Best WordPress Twitter Widgets
/ -2
-220+ Best WordPress Booking and Reservation Plugins
/ 3
3February, 2021
Working With Tables in React: Part Two
/ -1
-1Best CSS Animations and Effects on CodeCanyon
/ -15
-1530 CSS Best Practices for Beginners
/ -3
-3How to Create a Custom WordPress Plugin From Scratch
/ -3
-3May, 2020
10 Best Responsive HTML5 Sliders for Images and Text… and 3 Free Options
/ -1
-116 Best Tab and Accordion Widget Plugins for WordPress
/ -4
-4April, 2020
18 Best WordPress Membership Plugins and 5 Free Plugins
/ -2
-225 Best WooCommerce Plugins for Products, Pricing, Payments and More
/ 3
310 Best WordPress Twitter Widgets
1 / 8
8March, 2020
12 Best Contact Form PHP Scripts for 2020
/ -6
-6September, 2017
February, 2020
20 Popular WordPress User Interface Elements
/ -3
-310 Best WordPress Star Rating Plugins
/ -8
-8January, 2020
12 Best CSS Animations on CodeCanyon
/ -2
-212 Best WordPress Booking and Reservation Plugins
/ -2
-220 Best WordPress Calendar Plugins and Widgets
/ -1
-1December, 2019
12 Elegant CSS Pricing Tables for Your Latest Web Project
/ 5
524 Best WordPress Form Plugins for 2020
/ 2
2September, 2019
14 Best PHP Event Calendar and Booking Scripts
/ -3
-3July, 2019
Create a Blog for Each Category or Department in Your WooCommerce Store
/ 5
5April, 2019
8 Best WordPress Booking and Reservation Plugins
/ -10
-10March, 2019
Best Exit Popups for WordPress Compared
/ 16
16Best Exit Popups for WordPress Compared
/ -8
-811 Best Tab & Accordion WordPress Widgets & Plugins
/ -11
-1112 Best Tab & Accordion WordPress Widgets & Plugins
1February, 2019
New Course: Practical React Fundamentals
/ 2
2January, 2019
Short Course: Better Angular App Architecture With Modules
/ 2
2Preview Our New Course on Angular Material
/ 2
2Build Your Own CAPTCHA and Contact Form in PHP
/ -4
-4December, 2018
Object-Oriented PHP With Classes and Objects
/ -6
-6Best Practices for ARIA Implementation
/ -2
-2Accessible Apps: Barriers to Access and Getting Started With Accessibility
/ -5
-5November, 2018
Dramatically Speed Up Your React Front-End App Using Lazy Loading
/ 19
19October, 2018
15 Best Modern JavaScript Admin Templates for React, Angular, and Vue.js
/ -7
-715 Best Modern JavaScript Admin Templates for React, Angular and Vue.js
/ 2
219 Best JavaScript Admin Templates for React, Angular, and Vue.js
/ 2
2New Course: Build an App With JavaScript and the MEAN Stack
/ 3
3Hands-on With ARIA: Accessibility Recipes for Web Apps
/ 1
110 Best WordPress Facebook Widgets
13 / -1
-1September, 2018
Hands-on With ARIA: Accessibility for eCommerce
/ -2
-2New eBooks Available for Subscribers
/ -5
-5Hands-on With ARIA: Homepage Elements and Standard Navigation
/ 13
13-
/
 -3
-3 August, 2018
How Secure Are Your JavaScript Open-Source Dependencies?
/ -3
-3New Course: Secure Your WordPress Site With SSL
/ -5
-5Testing Components in React Using Jest and Enzyme
/ -11
-11Testing Components in React Using Jest: The Basics
/ -4
-4July, 2018
15 Best PHP Event Calendar and Booking Scripts
/ -1
-1June, 2018
Create Interactive Gradient Animations Using Granim.js
/ 13
13How to Build Complex, Large-Scale Vue.js Apps With Vuex
1 / -7
-7Examples of Dependency Injection in PHP With Symfony Components
/ -4
-4May, 2018
Set Up Routing in PHP Applications Using the Symfony Routing Component
1 / 11
11A Beginner’s Guide to Regular Expressions in JavaScript
/ 8
8Introduction to Popmotion: Custom Animation Scrubber
/ -7
-7Introduction to Popmotion: Pointers and Physics
/ -15
-15New Course: Connect to a Database With Laravel’s Eloquent ORM
/ -11
-11How to Create a Custom Settings Panel in WooCommerce
/ -9
-9Building the DOM faster: speculative parsing, async, defer and preload
1 / 1
120 Useful PHP Scripts Available on CodeCanyon
3 / 45
45April, 2018
How to Find and Fix Poor Page Load Times With Raygun
/ 5
5Introduction to the Stimulus Framework
/ -6
-6Single-Page React Applications With the React-Router and React-Transition-Group Modules
/ -1
-1-
/
 4
4 12 Best Contact Form PHP Scripts
1 / -2
-2Getting Started With the Mojs Animation Library: The ShapeSwirl and Stagger Modules
/ 4
4Getting Started With the Mojs Animation Library: The Shape Module
/ 4
4Getting Started With the Mojs Animation Library: The HTML Module
/ 4
4Project Management Considerations for Your WordPress Project
/ -2
-28 Things That Make Jest the Best React Testing Framework
/ 6
6March, 2018
Creating an Image Editor Using CamanJS: Layers, Blend Modes, and Events
/ -2
-2New Short Course: Code a Front-End App With GraphQL and React
/ 3
3Creating an Image Editor Using CamanJS: Applying Basic Filters
/ -6
-6Creating an Image Editor Using CamanJS: Creating Custom Filters and Blend Modes
/ -1
-1Modern Web Scraping With BeautifulSoup and Selenium
/ 3
3Challenge: Create a To-Do List in React
1 / 1
1Deploy PHP Web Applications Using Laravel Forge
/ -2
-2Getting Started With the Mojs Animation Library: The Burst Module
/ -3
-3-
/
 -6
-6 10 Things Men Can Do to Support Women in Tech
/ 1
1February, 2018
A Gentle Introduction to Higher-Order Components in React: Best Practices
/ -3
-3A Gentle Introduction to HOC in React: Learn by Example
/ 1
1A Gentle Introduction to Higher-Order Components in React
/ -5
-5Creating Pretty Popup Messages Using SweetAlert2
/ -3
-3Creating Stylish and Responsive Progress Bars Using ProgressBar.js
/ 10
1018 Best Contact Form PHP Scripts for 2022
/ -1
-1How to Make a Real-Time Sports Application Using Node.js
/ -1
-1Creating a Blogging App Using Angular & MongoDB: Delete Post
/ -14
-14Set Up an OAuth2 Server Using Passport in Laravel
/ 6
6Creating a Blogging App Using Angular & MongoDB: Edit Post
/ -2
-2Creating a Blogging App Using Angular & MongoDB: Add Post
/ 2
2Introduction to Mocking in Python
/ -2
-2Creating a Blogging App Using Angular & MongoDB: Show Post
/ 10
10Creating a Blogging App Using Angular & MongoDB: Home
/ 7
7-
/
 3
3 Creating a Blogging App Using Angular & MongoDB: Login
/ 12
12Creating Your First Angular App: Implement Routing
/ 5
5Persisted WordPress Admin Notices: Part 4
/ -6
-6Creating Your First Angular App: Components, Part 2
/ -3
-3Persisted WordPress Admin Notices: Part 3
/ 4
4Creating Your First Angular App: Components, Part 1
/ 1
1How Laravel Broadcasting Works
/ 6
6-
/
 11
11 Persisted WordPress Admin Notices: Part 2
/ -7
-7Create Your First Angular App: Storing and Accessing Data
/ 7
7Persisted WordPress Admin Notices: Part 1
/ -2
-2Error and Performance Monitoring for Web & Mobile Apps Using Raygun
/ 5
5Using Luxon for Date and Time in JavaScript
7 / -4
-4January, 2018
How to Create an Audio Oscillator With the Web Audio API
/ -6
-6How to Cache Using Redis in Django Applications
/ 4
420 Essential WordPress Utilities to Manage Your Site
/ -10
-10Introduction to API Calls With React and Axios
/ 3
3Beginner’s Guide to Angular 4: HTTP
/ 14
14Rapid Web Deployment for Laravel With GitHub, Linode, and RunCloud.io
/ 7
7Beginners Guide to Angular 4: Routing
/ -11
-11Beginner’s Guide to Angular 4: Services
/ -3
-3Beginner’s Guide to Angular 4: Components
/ 4
4Creating a Drop-Down Menu for Mobile Pages
/ 6
6Introduction to Forms in Angular 4: Writing Custom Form Validators
/ 5
510 Best WordPress Booking & Reservation Plugins
/ -5
-5Getting Started With Redux: Connecting Redux With React
/ 7
7Getting Started With Redux: Learn by Example
/ 9
9Getting Started With Redux: Why Redux?
/ 6
6Understanding Recursion With JavaScript
/ -1
-1How to Auto Update WordPress Salts
/ -5
-5How to Download Files in Python
/ 5
5-
/
 -15
-15 Eloquent Mutators and Accessors in Laravel
1 / 12
12-
/
 -10
-10 December, 2017
-
/
 15
15 10 Best HTML5 Sliders for Images and Text
/ 6
6Creating a Task Manager App Using Ionic: Part 2
/ 2
2Creating a Task Manager App Using Ionic: Part 1
/ -1
-1Introduction to Forms in Angular 4: Reactive Forms
/ -2
-2-
/
 -4
-4 Introduction to Forms in Angular 4: Template-Driven Forms
/ 1
124 Essential WordPress Utilities to Manage Your Site
/ 3
325 Essential WordPress Utilities to Manage Your Site
/ -7
-7Get Rid of Bugs Quickly Using BugReplay
1 / -20
-20Manipulating HTML5 Canvas Using Konva: Part 1, Getting Started
/ 2
210 Must-See Easy Digital Downloads Extensions for Your WordPress Site
22 Best WordPress Booking and Reservation Plugins
/ -2
-2Understanding ExpressJS Routing
/ -5
-515 Best WordPress Star Rating Plugins
/ 8
8Creating Your First Angular App: Basics
/ -6
-6November, 2017
Inheritance and Extending Objects With JavaScript
/ -9
-9Introduction to the CSS Grid Layout With Examples
1-
/
 3
3 Performant Animations Using KUTE.js: Part 5, Easing Functions and Attributes
/ -4
-4Performant Animations Using KUTE.js: Part 4, Animating Text
/ -4
-4Performant Animations Using KUTE.js: Part 3, Animating SVG
/ -9
-9New Course: Code a Quiz App With Vue.js
/ -1
-1Performant Animations Using KUTE.js: Part 2, Animating CSS Properties
-
/
 2
2 Performant Animations Using KUTE.js: Part 1, Getting Started
/ 3
310 Best Responsive HTML5 Sliders for Images and Text (Plus 3 Free Options)
/ -7
-7Single-Page Applications With ngRoute and ngAnimate in AngularJS
/ -11
-11Deferring Tasks in Laravel Using Queues
/ -5
-5-
/
 2
2 Site Authentication in Node.js: User Signup and Login
/ 4
4Working With Tables in React, Part Two
/ -14
-14Working With Tables in React, Part One
/ -1
-1How to Set Up a Scalable, E-Commerce-Ready WordPress Site Using ClusterCS
/ -6
-6New Course on WordPress Conditional Tags
/ 3
3October, 2017
TypeScript for Beginners, Part 5: Generics
/ 2
2-
/
 -8
-8 Building With Vue.js 2 and Firebase
6 / 12
12-
/
 -8
-8 -
/
 1
1 Best Unique Bootstrap JavaScript Plugins
/ 1
1Essential JavaScript Libraries and Frameworks You Should Know About
/ 5
5-
/
 5
5 Vue.js Crash Course: Create a Simple Blog Using Vue.js
/ -16
-16Build a React App With a Laravel RESTful Back End: Part 1, Laravel 5.5 API
/ 3
3API Authentication With Node.js
/ -4
-4Beginner’s Guide to Angular: HTTP
/ 1
1Beginner’s Guide to Angular: Routing
/ -3
-3Beginners Guide to Angular: Routing
/ -6
-6Beginner’s Guide to Angular: Services
/ 6
6Beginner’s Guide to Angular: Components
/ 2
2September, 2017
How to Create a Custom Authentication Guard in Laravel
/ 7
7Learn Computer Science With JavaScript: Part 3, Loops
/ -7
-7Build Web Applications Using Node.js
/ 2
2Learn Computer Science With JavaScript: Part 4, Functions
/ 3
3Learn Computer Science With JavaScript: Part 2, Conditionals
/ 13
13Learn Computer Science With JavaScript: Part 1, The Basics
/ 1
1Create Interactive Charts Using Plotly.js, Part 5: Pie and Gauge Charts
/ -7
-7Create Interactive Charts Using Plotly.js, Part 4: Bubble and Dot Charts
/ 3
3Create Interactive Charts Using Plotly.js, Part 3: Bar Charts
/ -10
-10Awesome JavaScript Libraries and Frameworks You Should Know About
/ 1
1Create Interactive Charts Using Plotly.js, Part 2: Line Charts
/ -11
-11Bulk Import a CSV File Into MongoDB Using Mongoose With Node.js
/ -4
-4Getting Started With End-to-End Testing in Angular Using Protractor
/ 8
8TypeScript for Beginners, Part 4: Classes
/ -8
-8Object-Oriented Programming With JavaScript
/ 5
5Stateful vs. Stateless Functional Components in React
/ 9
9Make Your JavaScript Code Robust With Flow
/ -1
-1Build a To-Do API With Node and Restify
/ 7
7Testing Components in Angular Using Jasmine: Part 2, Services
/ 2
2Testing Components in Angular Using Jasmine: Part 1
/ -2
-2Creating a Blogging App Using React, Part 6: Tags
/ -14
-14August, 2017
React Crash Course for Beginners, Part 3
/ 5
5React Crash Course for Beginners, Part 2
/ 1
1React Crash Course for Beginners, Part 1
/ 4
4Set Up a React Environment, Part 4
1 / 10
10Set Up a React Environment, Part 3
/ -2
-2New Course: Get Started With Phoenix
/ -5
-5Set Up a React Environment, Part 2
/ 3
3Set Up a React Environment, Part 1
/ -4
-4Command Line Basics and Useful Tricks With the Terminal
/ 5
5How to Create a Real-Time Feed Using Phoenix and React
/ -1
-1Build a React App With a Laravel Back End: Part 2, React
/ -2
-2Build a React App With a Laravel RESTful Back End: Part 1, Laravel 9 API
/ -3
-3Creating a Blogging App Using React, Part 5: Profile Page
/ -4
-4Pagination in CodeIgniter: The Complete Guide
/ 23
23JavaScript-Based Animations Using Anime.js, Part 4: Callbacks, Easings, and SVG
JavaScript-Based Animations Using Anime.js, Part 3: Values, Timeline, and Playback
/ 2
2Learn to Code With JavaScript: Part 1, The Basics
/ -3
-3July, 2017
10 Elegant CSS Pricing Tables for Your Latest Web Project
/ -12
-12Getting Started With the Flux Architecture in React
/ -2
-2Getting Started With Matter.js: The Composites and Composite Modules
/ -1
-1Getting Started With Matter.js: The Engine and World Modules
/ 12
1210 More Popular HTML5 Projects for You to Use and Study
/ -19
-19Understand the Basics of Laravel Middleware
/ -3
-3Iterating Fast With Django & Heroku
/ 13
13Creating a Blogging App Using React, Part 4: Update & Delete Posts
Creating a jQuery Plugin for Long Shadow Design
/ -11
-11How to Register & Use Laravel Service Providers
2 / -7
-7Unit Testing in React: Shallow vs. Static Testing
/ 1
1Creating a Blogging App Using React, Part 3: Add & Display Post
/ 8
8June, 2017
Creating a Blogging App Using React, Part 2: User Sign-Up
20Creating a Blogging App Using React, Part 1: User Sign-In
/ -2
-29 More Popular HTML5 Projects for You to Use and Study
/ 1
1Creating a Grocery List Manager Using Angular, Part 2: Managing Items
/ 3
39 Elegant CSS Pricing Tables for Your Latest Web Project
/ -5
-5Dynamic Page Templates in WordPress, Part 3
/ -1
-1Angular vs. React: 7 Key Features Compared
/ 5
5Creating a Grocery List Manager Using Angular, Part 1: Add & Display Items
/ -1
-1New eBooks Available for Subscribers in June 2017
/ 3
3Create Interactive Charts Using Plotly.js, Part 1: Getting Started
/ 9
9The 5 Best IDEs for WordPress Development (And Why)
/ -3
-333 Popular WordPress User Interface Elements
/ -2
-2New Course: How to Hack Your Own App
/ -8
-8How to Install Yii on Windows or a Mac
/ -4
-4What Is a JavaScript Operator?
/ -2
-2How to Register and Use Laravel Service Providers
/ 7
7


waly Good blog post. I absolutely love this…